Synthesis of Robotic Actions
A novel approach to action synthesis is proposed by leveraging movement primitives learned through neural networks models. The work introduces a method for adapting actions to the environment based on demonstrated ones, then combining them in the correct order to achieve different goals.
In the research, action synthesis is achieved through the concatenation of basic primitives, spatial interpolation, and the network’s ability to encode multidimensional data to embed the environment representation.
The result is the generation of a long-term sequence of actions adapted to the environment to achieve different tasks requested.
In simple terms:
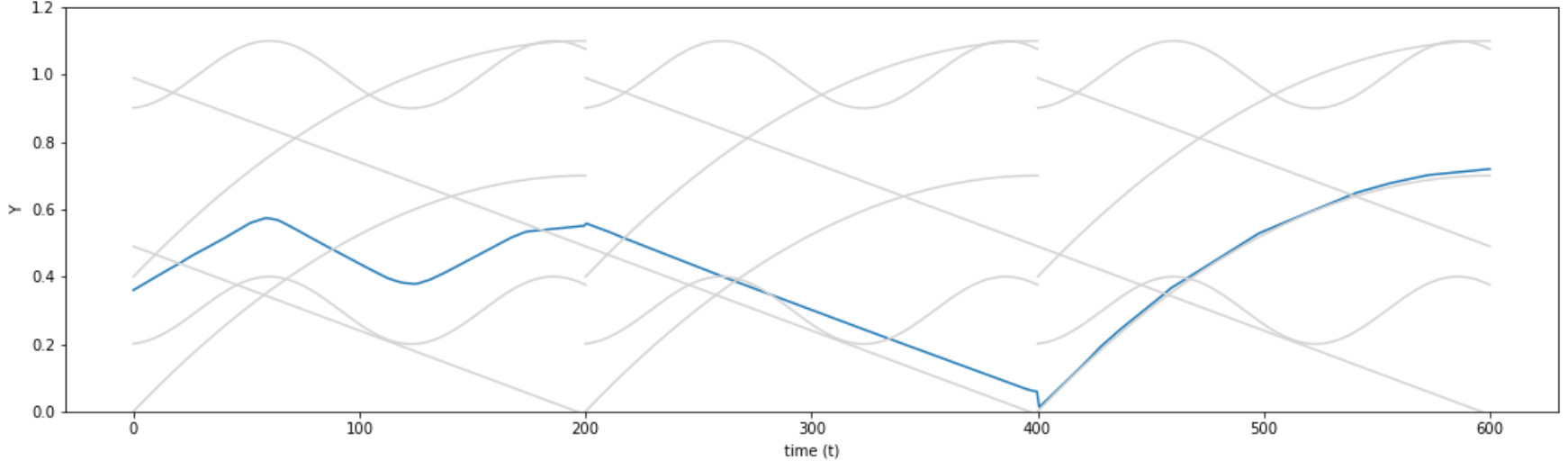
The model is trained with different actions. (example: push, jump over, go through)(we will simplify also them as a single value in time). It is possible to condition an action generated by the neural-network model to a certain point in time (eg. where to start, end, or pass). The model also predicts the end status after executing that action.
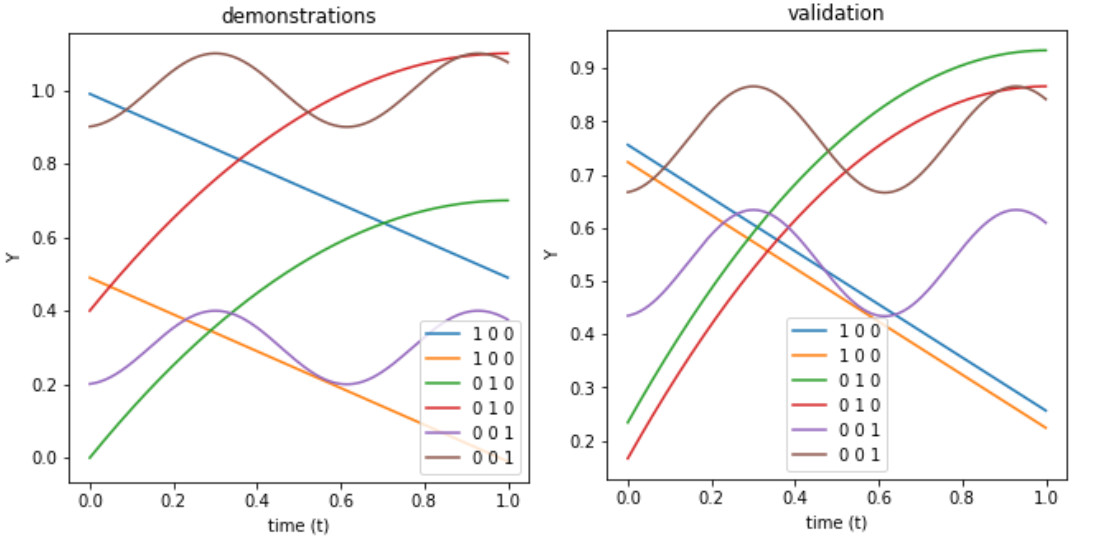
From the starting position (or also environment status), all actions possible are computed from this state. The network adapts to the current state generalizing from the previously taught actions. Subsequently, all next actions possible are computed from the results of the previous actions.
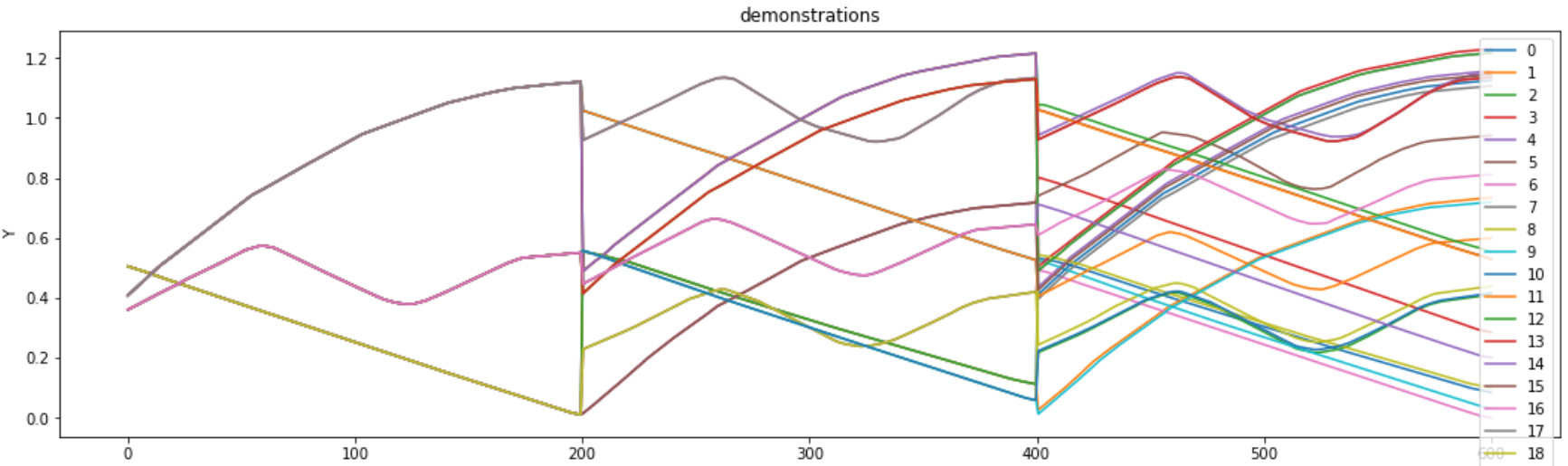
The tree of chained actions possibilities is filtered when the actions fail to meet a criteria (will not be possible or not make sense).
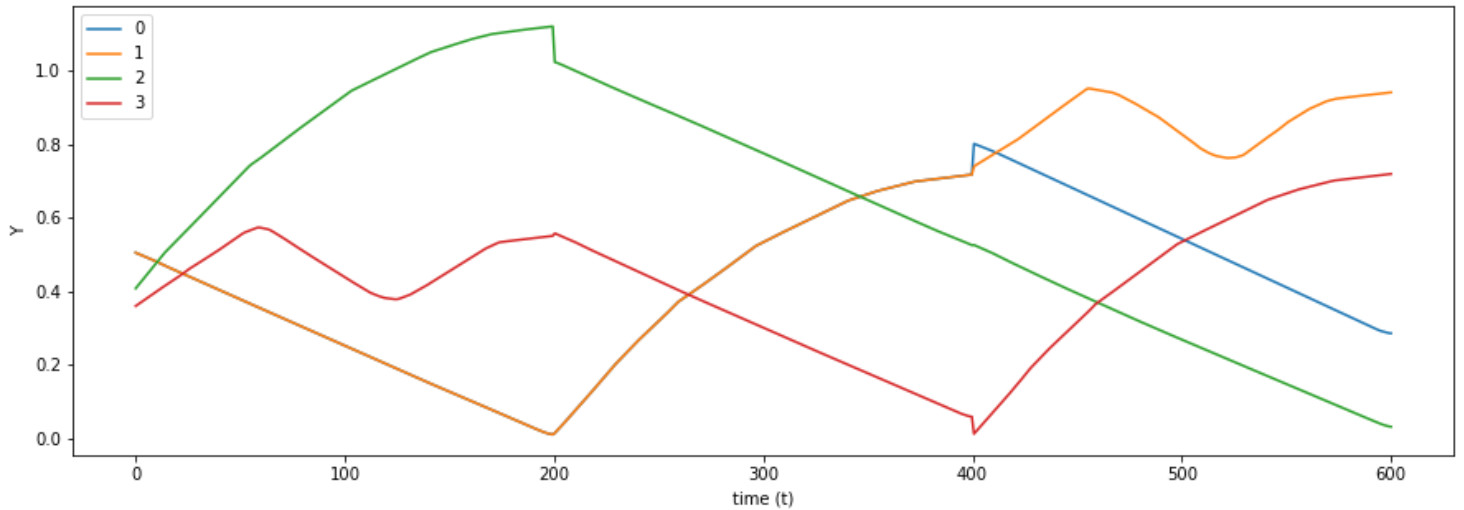
Now, all the real possibilities and results of combining different simple actions are clear. The correct sequence that reaches the desired goal is identified and executed.
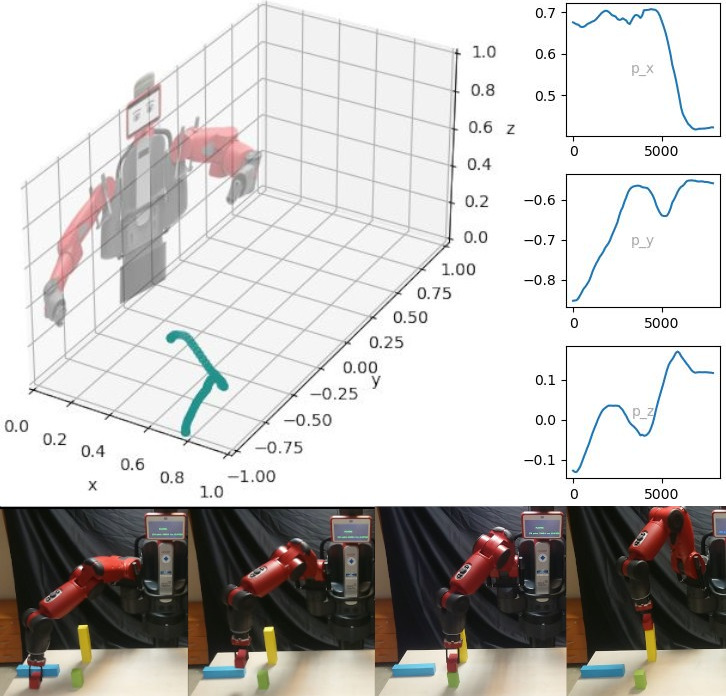
Testing
The model is tested on the Baxter Robot. Different actions are taught by demonstration and the Conditional Neural Motion Planning (CNMP) network is trained on those skills.
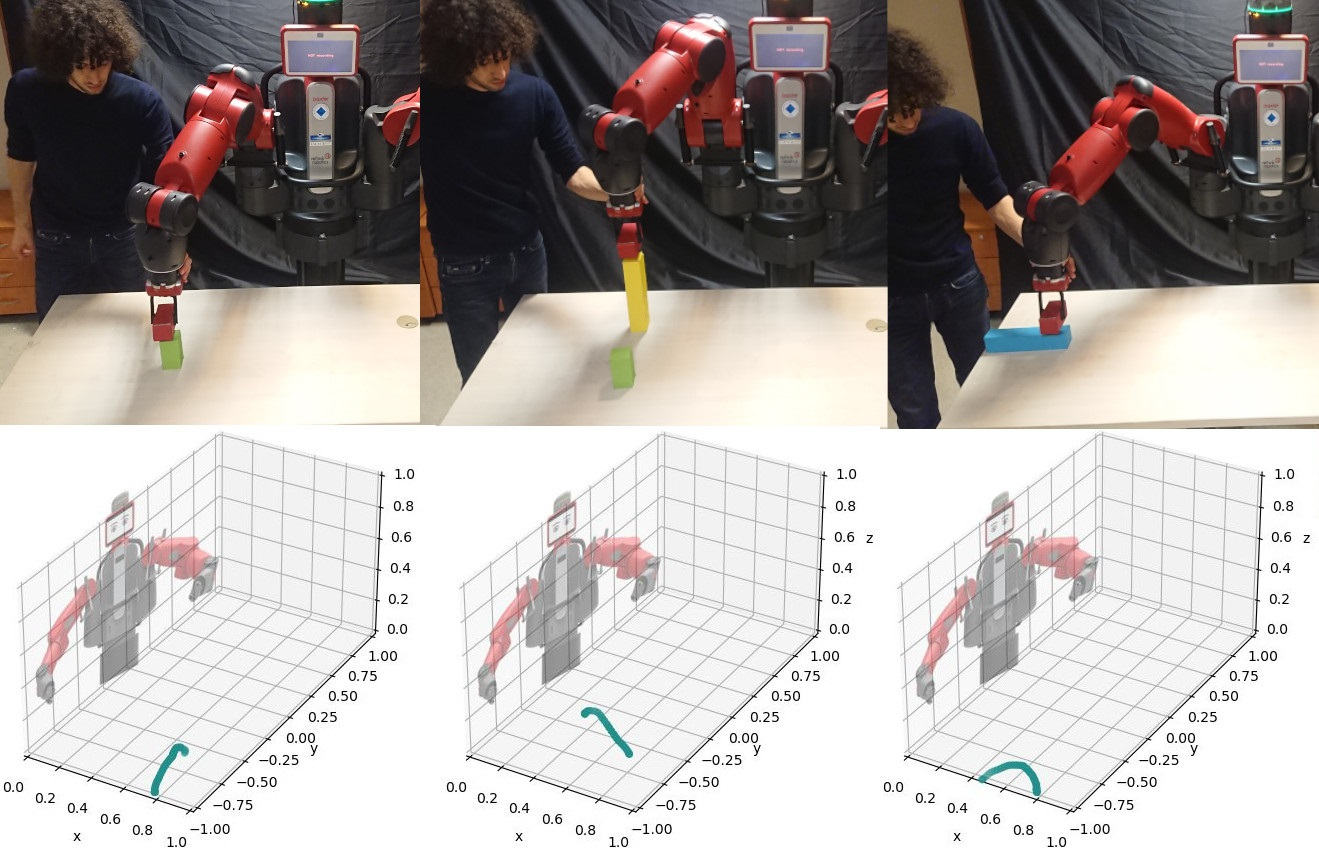
Subsequently, the method adapts them spatially to the environment and finds the correct sequence to complete the goal. The sequence was never explicitly taught by the expert.
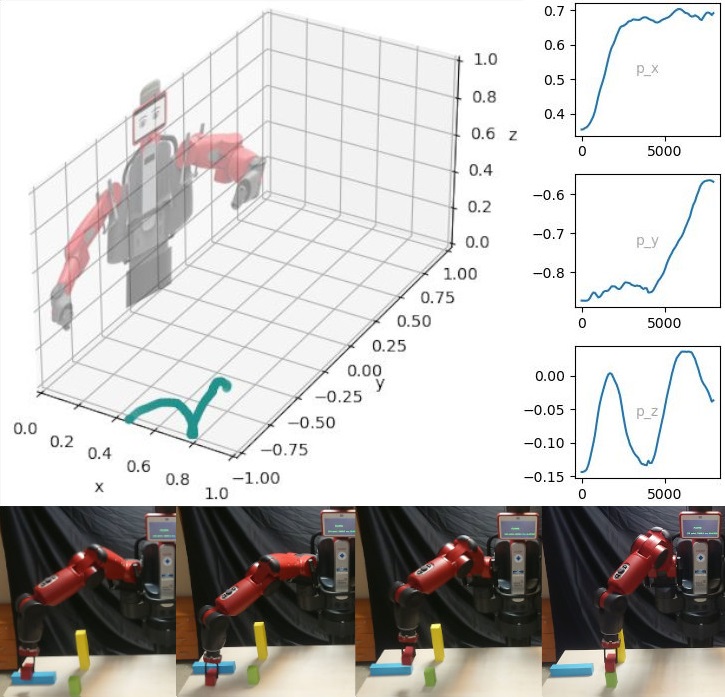
The method allows the flexibility of achieving different goals (an exponential number of them) using the base knowledge of actions learned.